SSC GD Exam Pattern 2026: Marking Schema and PET/PST Exam Pattern
SSC released the notification for the recruitment of SSC General Duty Constable on 1st December. More than 25,000 vacancies have been released to recruit constables for the paramilitary forces like BSF, CISF, CRPF, SSB, ITBP, AR, SSF, and NCB. All the 10th pass candidates who are interested in applying for this role should be aware of the exam pattern and the selection process. In this blog, we will discuss the SSC GD Exam Pattern, Physical Efficiency Test and Physical Standards in detail.
SSC GD Exam Pattern 2026
The SSC GD exam pattern starts with a written examination. This exam is conducted online and multiple-choice questions are asked. There are 4 sections in the exam with General Intelligence & Reasoning, General Knowledge & General Awareness, Elementary Mathematics, and English/ Hindi as the subjects. There is a total of 80 questions, with 20 questions per section, which account for 160 marks. There is a negative marking 0f 0.25 marks for every wrong answer. The exam is conducted in 15 language including English, Hindi and 13 Regional languages (Assamese, Bengali, Gujarati, Kannada, Konkani, Malayalam, Manipuri, Marathi, Odia, Punjabi, Tamil, Telugu, and Urdu)
|
SSC GD Exam Pattern 2026 |
||||
|
Sno. |
Subjects |
No. of Questions |
Maximum Marks |
Exam Duration |
|
1 |
General Intelligence & Reasoning |
20 |
40 |
1 hour (60 minutes) |
|
2 |
General Knowledge & General Awareness |
20 |
40 |
|
|
3 |
Elementary Mathematics |
20 |
40 |
|
|
4 |
English/ Hindi |
20 |
40 |
|
|
Total |
80 |
160 |
||
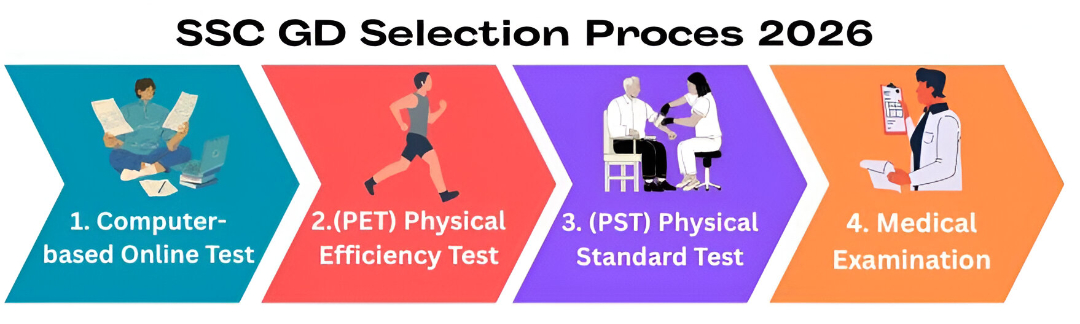
SSC GD Constable Selection Stages 2026
The SSC GD Constable selection process consists of five following stages:
1. Computer Based Test (CBT)
2. Physical Efficiency Test (PET)
3. Physical Standard Test (PST)
4. Medical Examination
5. Document Verification
SSC GD Minimum Qualifying Marks Criteria
To be able to move forward in the recruitment process, applicants have to score more than the minimum qualifying marks fixed by SSC. These marks are different for different categories. The table below shows the minimum qualifying marks criteria for the CBT exam:
|
Categories |
Minimum Qualifying Marks |
|
UR |
30% |
|
OBC/EWS |
25% |
|
All Other Categories |
20% |
SSC GD Exam Pattern for PET/PST
After qualifying the CBT, candidates have to appear for the PET/PST stage, which is checks the physical fitness of the candidates and ensures that they meet the prescribed body standards. Only candidates who clear both PET and PST move to the medical examination stage.
SSC GD Physical Efficiency Test (PET) Exam Pattern
This assessment is crucial for the recruitment process because it ensures that all the selected candidates have the strength to handle the demanding duties of a General Duty Constable, as this role involves long hours, patrolling and other operational responsibilities.
The Physical Efficiency Test (PET) involves a race which has to be finished within a time limit. The tables given below discuss the details of the test for both male and female candidates:
|
Race for Male Candidates |
|
|
Type |
Male |
|
Candidates other than Ladakh Region |
5 Km in 24 minutes |
|
For Ladakh Region |
1.6 Km in 7 minutes |
|
Race for Female Candidates |
|
|
Type |
Female |
|
Candidates other than Ladakh Region |
1.6 Km in 8½ minutes |
|
For Ladakh Region |
800 metres in 5 minutes |
SSC GD Physical Standard Test (PST) Exam Pattern
The Physical Standard Test (PST) measures height, weight, chest, and vision as per SSC norms. This examination is carried out under the supervision of trained officials using standard instruments. Claims for adjustments or re-measurement will not be entertained. Therefore, candidates are strongly advised to check the SSC GD physical requirements in advance and be prepared according to that before appearing for the exam.
|
Category |
Height (Male) |
Height (Female) |
|
General |
170 cm |
157 cm |
|
Scheduled Tribes |
162.5 cm |
150 cm |
|
Scheduled Tribes of NE States |
157 cm |
147.5 cm |
|
LWE Affected Districts |
160 cm |
147.5 cm |
|
Kumaonis, Garwalis, Marathas, Dogras, Assam, J&K, HP, Ladakh |
165 cm |
155 cm |
|
North-East States (Arunachal Pradesh, Meghalaya, Manipur, Mizoram, Nagaland, Tripura, Sikkim) |
162.5 cm |
152.5 cm |
|
Gorkha Territorial Administration (GTA), Darjeeling |
157 cm |
152.5 cm |
SSC GD Exam Pattern Official link
Physical Standard Test: Chest Measurement Criteria
The chest measurement test in the PST stage is only applicable for the male candidates. Candidate’s chest measurement and expansion play an important role in the qualifying this test. The following table discusses the category-wise chest size criteria:
|
CHEST (in cm) [Minimum Expansion- 5 cm] |
|
|
General, SC & OBC |
80 cm |
|
All candidates belonging to the Scheduled Tribes |
76 cm |
|
Candidates falling in the categories of Garhwalis, Kumaonis, Dogras, Marathas and candidates belonging to the States/ UTs of Assam, Himachal Pradesh, Jammu & Kashmir and Ladakh |
78 cm |
|
|
|
|
Candidates hailing from the North-Eastern States of Arunachal Pradesh, Manipur, |
77 cm |
|
Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Sikkim, Tripura and Gorkha Territorial Administration (GTA) |
|
Visual Ability Requirements for PST
The Physical Standard Test also includes eyesight. Candidates have to meet the specified visual standards to move to the next stage. The table given below discusses the details of the visual standards:
|
Visual Standards |
|||||
|
Visual Acuity Unaided |
Visual Acuity Unaided |
Refraction |
Color Vision |
||
|
Near Vision |
Distant Vision |
Visual correction of any kind is not permitted even by glasses |
CP-2 |
||
|
Better Eye |
Worse Eye |
Better Eye |
Worse Eye |
||
|
N6 |
N9 |
06-Jun |
06-Sep |
||